Decentralized applications, otherwise known as ‘DApps’/’dApps’, are all the rave in the cryptocurrency and blockchain sector at the moment. While cryptocurrency returns have slowed down, DApps have been generating significant amounts of volume, crossing an average of approximately $30M USD equivalent and making many people wealthy.
Whether you’re an established company looking for a proposed faster, cheaper alternative to centralized databases, or simply a cryptocurrency enthusiast looking to utilize DApps to gain some extra cash flow, it can be a challenging concept to grasp. As a result, we’ve created this guide as a means of facilitating the DApp learning curve. Read our guide to find out what DApps are,
Prior to starting, we highly advise you take a look at our previous guides that go over how to buy Bitcoin and get started with cryptocurrency as well as overviewing Ethereum blockchain basics. This is necessary for this guide as we’ll be talking about preliminary basic crypto and blockchain concepts that if you’re not familiar with, may get confusing. We would also like to note that DApps are complex technologies: If you get lost, confused, or stuck don’t hesitate to reach out to us, we’re happy to help.
What is a Decentralized Application (DApp)?
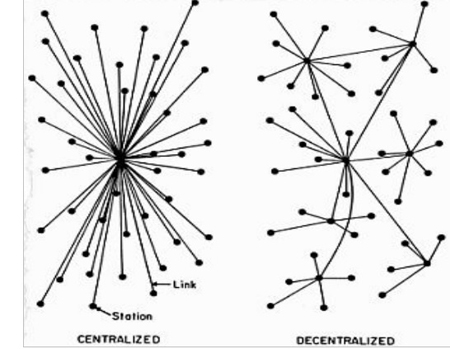
To understand what DApps are, you need to first look at what network decentralization is (It’s a fancy word for something we’ll break down into very basic pieces). –> Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency that runs in a ‘decentralized manner’; that means it has no central database that processes anything that happens in relation to Bitcoin’s framework; rather, users on Bitcoin work together via their computers (In a passive way) on Bitcoin’s network to process things immediately just by using Bitcoin. No central authority governs, determines the price of, or maintains Bitcoin. One project, in particular, saw Bitcoin’s technology and realized that this decentralization concept could be applied to infinite amounts of industries and change finance forever. The project was named Ethereum: Their project was a cryptocurrency named ‘Ether’ that served as the fuel for an infrastructure that could run modern-day applications on their inclusive blockchain, birthing what’s now known as decentralized applications (DApps for short).
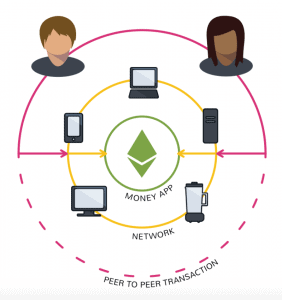
DApps can be easily understood when compared to existing applications, for example, such as Uber. First, let’s assess the visual component of DApps. DApps are reliant on multiple ‘parties’ to process things, not just one. Centralized apps are reliant upon one centralized ‘party’ to process things.
Let’s look at how Uber works (It might seem like we’re getting into highly complex topics, but stick with us, it’s not as complicated as you might think).
Uber is a centralized, ride-hailing application. It is commonly used as a cross example to portray how apps can be decentralized. If you need a ride somewhere you open Uber, specify where you’re going, pay with your credit card, and Uber keeps a sizable fee. An Uber driver will then pick you up to drop you off at y0ur destination, and then mark your arrival on the app. In each of these instances, centralization is heavily apparent. The singular central system can dictate everything on the platform without approval from others and without any type of verification. One person, or owner, has the rightful functionality to control the entire digital environment; of course, there are other centralized processes that are piled on to one another to make things more ‘secure’ and fair. Some firms do a great job at this, however, at its absolute core, a centralized application is still vulnerable to centralized-focused attacks, no many how many central protection layers you put on it.
DApps were created with a goal of ‘cutting out middlemen’ – take our example of Uber. Imagine Uber was developed in the structure of a decentralized application – there would be no central entity which means that the risk of hacking, fraud, and illegitimate processes on the app are spread out amongst infinite amounts of people. If Uber functioned as a DApp, consider the following which emphasizes how a DApp works:
➡️If you were a driver on this Uber DApp, you would connect to passengers who are requesting rides in real-time via the blockchain.
➡️Depending on the network, this would mean faster rides and higher levels of efficiency. Imagine if all the Uber’s currently active in New York City were enabled via a DApp, meaning a small percent of efficiency higher; this would save billions in dollars annually and would speed human productivity.
➡️On this imaginary Uber DApp, centralized fees don’t exist either. Since passengers and drivers are connecting directly with one another, there doesn’t need to be any fees at all.
➡️Drivers can keep 100% of their earnings and whoever develops the DApp can pursue alternative, better ways to maintain profit; this is done most commonly through proprietary platform cryptocurrencies.
In an app, many users use a central data center, however, with DApps, the users are the data center.
DApps are various; they have a large variety of targeted sectors. While there is a large global vision in mind for the future of DApps, current DApps must run on respective individual blockchains. There are currently 4 mainstream blockchains that comprise over 95% of all DApp volume that goes on at the moment. Those are, in order of volume (At the time of this writing – this can change by the day):
- Tron ($TRX) Blockchain
- EOS ($EOS) Blockchain
- iOST ($IOST) Blockchain
- Ethereum ($ETH) Blockchain
Advantages and Disadvantages of DApps
Advantages
- Function with no central authority
- Can process transactions/processes faster than centralized systems
- They are apps that are maintained by users just by using the application
- Ethereum was the first DApp platform, Tron is currently the most popular however
- Their goal is to ‘cut out the middlemen’ in central applications
Disadvantages
- Cryptocurrencies power DApps, but DApps are not cryptocurrencies
- Never 100% reliable and safe; there can be scam DApps
- They’re not instant get rich products although they did make many people wealthy last year
Tron Holds the Top Stop For DApp Volume
Tron currently holds the top spot for most DApp volume – this is arguably because the Tron blockchain can process more transactions at faster speeds than most blockchains and for near-zero transaction costs.
At the moment the entirety of the DApp atmosphere is majority based on online website DApps. These are websites that allow users to interact with the blockchain through the website in place. How does that work, and how can you interact with these DApps? What’s the best blockchain for DApps? Where do I start? We’ll answer all of these questions, and you’ll be quite surprised at how easy some of them can be answered.
How To Use DApps
DApps might seem very complex in their technology at first, and that can be true; however, DApps are in almost all cases created and designed to be easy for the end user. (This part may become a bit technical, but stick with us while we explain). We’re not going to go into the development aspect of DApps, just the plain overview from a basic user’s perspective.
At the moment, the most common form of DApps is via websites. Casinos and virtual collectible trading games are the two most common type of DApps at the moment. As a result, they are very similar to normal casino websites. If you go to a Tron Casino DApp, the process is still the same, you’re still trying to bet money for a return, however, with DApps you’re partaking in unison on the blockchain, and you’re betting cryptocurrency.
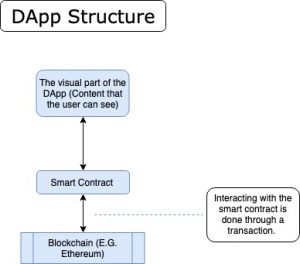
Most mainstream DApps you’ll see running on the blockchain consist of 3 main layers. As a user, it’s important to know these layers as one mistake can mean you lose all your funds (If you’re a developer that are much more layers involved).
The first layer of most DApps is the main website page: This is the neatly designed content, buttons, and search bars that you will interact with. The second layer is the library – this is essentially a type of technology that connects the website part of the DApp to the third layer, the most important one, which is: The smart contract. Each DApp will function on top of a smart contract. These smart contracts, once linked via a library, can be interacted with by you, the user.
As shown above, the 3 layers of the DApp will be used by us, the users, in a way that is easy to understand.
If you don’t know some of the definitions or concepts in the above image, don’t worry – things will become more clear as you read. Now let’s apply this same concept to finally using a DApp.
As a user, you first need a connection, better referenced as a link, to internet built DApps. This is a web browser extension that lets you connect to the blockchain through Chrome, Safari, and more; if you’re looking to start using a Tron DApp, we recommend TronLink, which in simple terms creates a Tron wallet for you that can interact directly with online DApps, accessible on your browser. Set up your account, and buy cryptocurrency, in this case, TRX (Or another cryptocurrency if you’re using a different blockchain DApp). EOS DApps require EOS to function, Ethereum DApps need Ether to function, etc.
Then, find a DApp you’re interested in; there’s a wide variety on Tron’s blockchain, however, always ensure that you’re at the correct domain addresses and not a fake DApp. Once your link is funded, find a DApp and try to interact with something. We created the following diagram to demonstrate how DApp interaction is traditionally done and used the most popular DApp currently TronBET as the primary example:
If done correctly, you’ll have successfully used a DApp. DApps range in purpose and platform; while a majority are gambling sites, many that are emerging are used for trading Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies in a decentralized manner. Another large niche market for DApps is virtual collectibles.
Comparing Different DApp Blockchains
Ethereum and its team were essentially the creators of retail and modern-day DApps that we see today. The goal of the Ethereum platform is to enable enterprises to build decentralized infrastructures using their infrastructure. Ethereum was fairly initially successful and garnered a large influx of mainstream attention when they released ‘Solidity’ their own programming language made to build ‘smart contracts’, the technology that powers DApps.
A few subsequent blockchains that started on Ethereum derived the DApp landscape entirely from the project. For example, Tron blockchain was at first built on Ethereum prior to migrating to its own blockchain. Tron smart contracts are most commonly created using Solidity.
Ethereum has run into scalability issues, however, and because of this, it has become one of the slower options for DApps. Developers have unfortunately opted not to go with Ethereum as their framework. Ethereum is, in fact, the father of the DApps that we see in today’s markets; however, it has unfortunately become one of the unpreferred options because of cost and transaction time.
Tron was not the first platform to enable development via decentralization on their blockchain, however, it’s at the moment the current DApp market leader. Tron’s blockchain has been, since the start of 2019, the leader in the following: Blockchain with most new DApps launched, Blockchain with most DApp volume, and the blockchain with the fastest DApp transaction settlements.
Tron, in March 2019, set the record for DApps when their blockchain reached $91 million in a single day’s transaction volume. Tron has a throughput of 2000 TPS, which means the Tron blockchain can process 2,000 transactions per second; keep in mind each interaction with a DApp is considered a transaction.
Tron currently houses the most popular DApps on the internet at the moment, with a large influx of volume from gambling and virtual collectible DApps.

EOS was one of Ethereum’s first competitors in terms of the DApp markets. EOS is a blockchain that runs on a DPoS model, a type of mechanism that enables an environment where there are zero transaction fees. This makes DApp interactions very worthwhile. In January 2018, Ethereum DApp volume reached all-time highs, however, transaction fees reached nearly $20 per transaction, and users would have to wait up to 30 minutes per interaction with a DApp. Subsequently, when EOS introduced their take on DApps featuring zero fees as well much faster transaction times, the entire market shifted towards EOS.
While EOS does, in fact, generate the #2 most volume in the DApp atmosphere, there are some users who are skeptical about its blockchain. While EOS claims over 4000 transactions per second, blockchain auditing firms have found rather they maintain about 250 transactions per second. In any case, EOS DApps are still continuing to garner attraction.
What makes EOS DApps unique? Well, unlike blockchains such as Ethereum or Tron where Solidity or similar languages are used for development, C++ is used to create EOS DApps. This is commonly regarded as the world’s most global programming language, so their integration of it opens opportunities for developers across the globe.
Best DApp Extensions and Tools
Best Ethereum DApp Extension
There are a few web browser extensions for Ethereum that are optimal for DApp interaction, however, none are quite as good as MetaMask. MetaMask was one of the first ever blockchain browser extensions and has maintained a viable track record.
MetaMask can be found on the Google Chrome web extension store as well as a few other verified locations as their official website.
MetaMask allows you to connect directly with Ethereum built DApps, and maintains fairly high security. The Ethereum team, as well as numerous other blockchain experts, have all named MetaMask as the go-to DApp browser extension for Ethereum DApps.
MetaMask also protects from malicious hacking attempts and employs fairly strict security.
DApps are forms of technology that are redefining the way that programs, companies, and platforms function. While they can be complicated at first, they have proven very efficient and can essentially cut costs and enable large efficiency on levels we haven’t seen before. Ensure you stay up to date with DApps by subscribing to InsideBitcoins and checking up on any cdaily content that we release!
FAQs
What are some of the best DApps?
DApp environments are changing constantly, however, currently, the most successful DApp in history that is still consistently establishing volume and user interactivity is TronBET, which is a gambling platform where you can bet your TRX.
Which DApp blockchain is the best?
There's no singular answer for which platform is best for DApps at the current stage since they are so new in their relative developments. At the moment, Tron is producing the most volume and user interaction than any other blockchain. iOST has similarly shown unprecedented growth, however, if you're looking more for stability and legacy status, Ethereum is a great option.
Are DApps just Ponzi schemes?
In the recent past, there have been multiple projects that function as DApps online that claim to offer a guaranteed return daily. This can range from 3.33% daily and above, we strongly advise you to stay away from these projects, as they are not sustainable and always fail. Not all DApps are Ponzi schemes, however. There are many legitimate projects out there, however, there are also fraudulent ones.
How do I access dividend yielding DApps?
Dividend yielding DApps are a new concept, in order to partake in these projects, you need to 'mine' the DApp's token, traditionally by playing a game, gambling, and overall just providing liquidity to the DApp. Once done, you'll be able to go to your 'Dividends' tab on the DApp and 'Freeze' your mined tokens. Then, depending on the dividend pool of the DApp, you'll be rewarded a certain amount of TRX passively.
Are DApps good sources of income?
DApps are not in any way definitively guaranteed to continue producing returns, dividends and the like. However, past results have shown that DApps have made early participants in now popular DApps very wealthy. For example, those who mined TronBET's ANTE token have received thousands of times return back on their investment for getting in on the DApp before it became the most visited one.