There’s probably no one who has never heard of Bitcoin. In recent years, the asset has witnessed a massive rise in its popularity and adoption. Hence, it is not surprising that many people are showing interest in everything that concerns the asset.
Meanwhile, as Bitcoin continues to dominate the crypto market, one of the most asked questions has always been about its next halving. Bloomberg, in its report, has already indicated that the next Bitcoin halving will unfold in April, 2024.
In this guide, we fully examine everything you need to know about Bitcoin halving. Read on to discover the factors that determine Bitcoin halving dates and many more.
What Is Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin halving is a fascinating and essential aspect of the Bitcoin network that plays a crucial role in regulating the supply of new BTCs. It is a scheduled event that occurs approximately every four years, or more precisely, after every 210,000 blocks have been added to the blockchain.
During this momentous event, the number of new BTCs generated per block is precisely halved, resulting in a significant reduction in the overall supply of new coins entering circulation. This deliberate reduction in supply, combined with the ongoing and often steady demand for Bitcoin, has historically proven to have a profound impact on the cryptocurrency’s price.
The concept of Bitcoin halving is an ingenious design within the Bitcoin protocol, put in place by its pseudonymous creator, Satoshi Nakamoto. It was ingeniously designed to ensure that the total supply of BTCs would ultimately reach its hard cap of 21 million coins.
By reducing the block rewards given to miners at regular intervals, the pace of creating new BTCs slows down, leading to a more controlled and predictable release of new coins into the market. This scarcity-driven model creates a unique dynamic that sets Bitcoin apart from traditional fiat currencies and many other cryptocurrencies.
To put it simply, imagine a scenario where BTCs are like a limited resource, gradually becoming scarcer over time. With each halving, the rate at which new coins are produced slows down, making the mining process more challenging and resource-intensive.
This process mirrors the characteristics of precious metals like gold, where their scarcity adds value and makes them desirable commodities. As a result, Bitcoin’s halving events have historically been associated with increased demand and soaring prices.
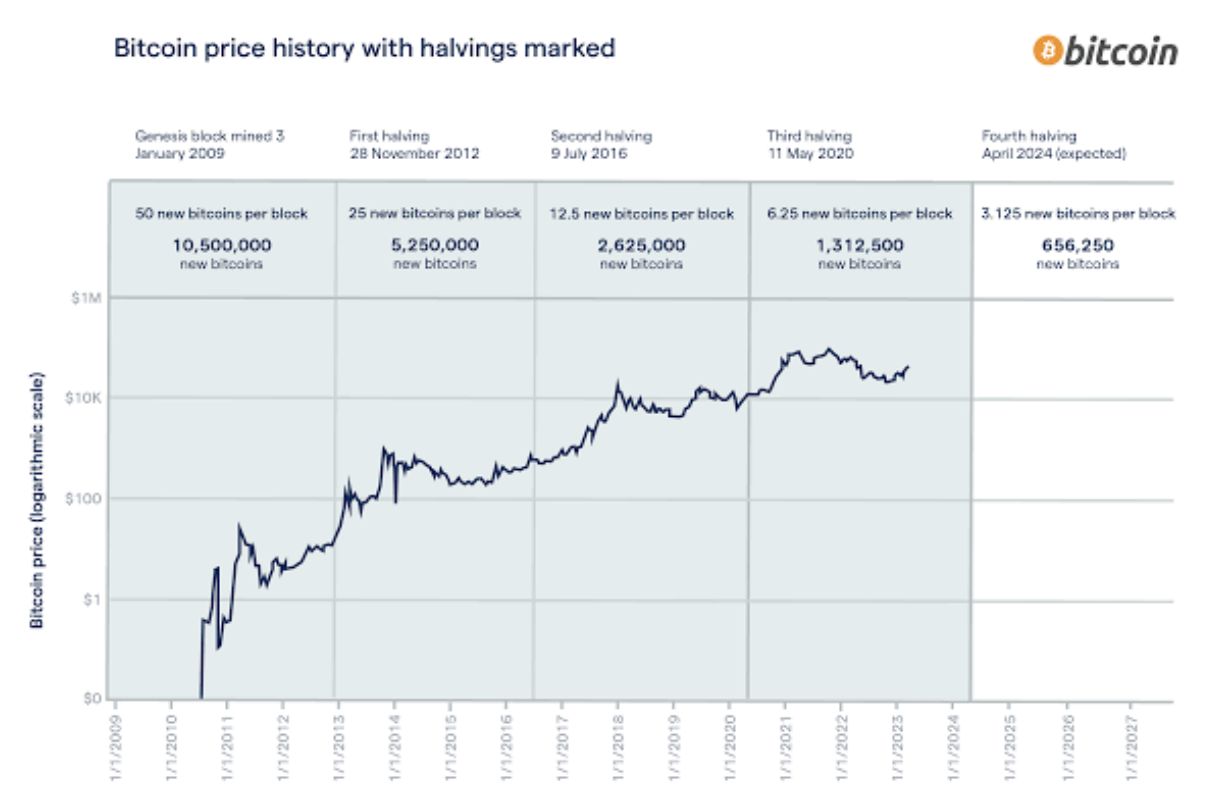
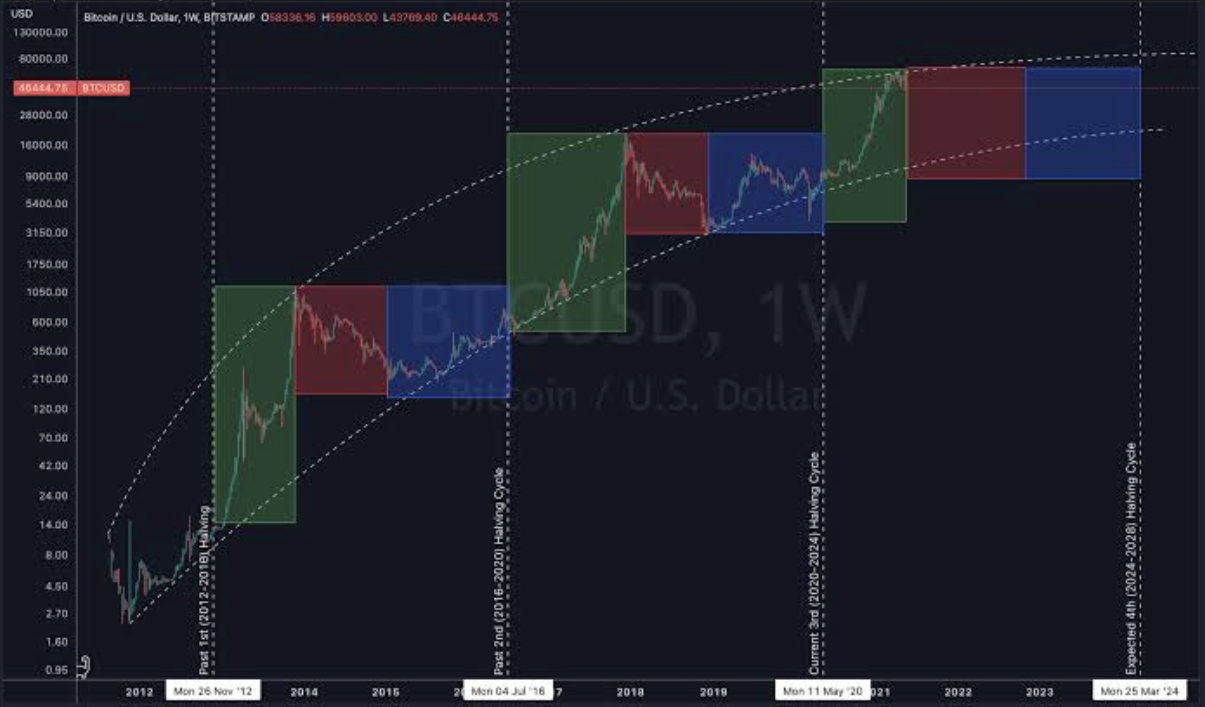
The first halving occurred in November 2012 when the block rewards dropped from 50 BTCs to 25 BTCs. The second halving took place in July 2016, further reducing the block rewards to 12.5 BTCs. Meanwhile, the most recent halving event happened on May 11, 2020, causing the block rewards to decrease to 6.25 BTCs per block.
Now, with the next Bitcoin halving scheduled to take place in 2024, there is considerable anticipation and excitement within the cryptocurrency community. As history has shown, each halving has been followed by substantial price increases, and many investors and analysts are closely monitoring the market in preparation for the next milestone event.
The Mathematics Behind Bitcoin Halving
At the core of Bitcoin’s unique monetary policy lies the concept of limited supply. Unlike traditional fiat currencies that can be endlessly printed by central banks, Bitcoin’s total supply is strictly capped at 21 million coins. This scarcity-driven model is one of the primary reasons for its appeal and value. However, achieving this scarcity mandates careful planning and the implementation of a sophisticated mathematical mechanism known as “Bitcoin halving.”
Bitcoin halving is a key feature built into the cryptocurrency’s protocol, designed to control the issuance of new BTCs and ensure a controlled release of coins into circulation. This mechanism is precisely programmed to occur approximately every four years or after every 210,000 blocks have been added to the blockchain. When a halving event occurs, the reward given to miners for adding new blocks to the blockchain is cut in half.
The underlying mathematical principle that governs halving is straightforward yet elegant. Each block in the Bitcoin blockchain contains a fixed number of transactions which is added to the chain approximately every 10 minutes. The reward for successfully mining a block, also known as the block reward, starts at a certain number of BTCs and is halved at regular intervals.
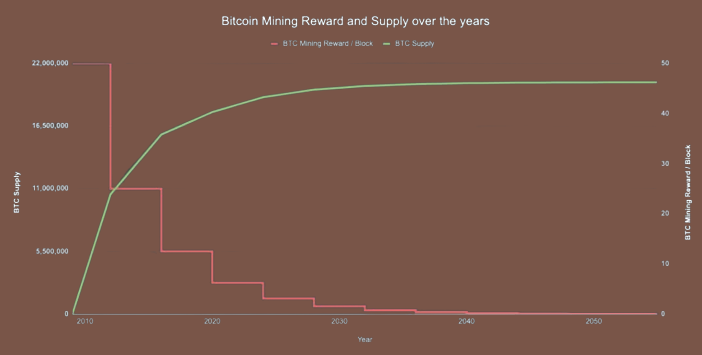
Initially, when Bitcoin was launched in 2009, the block reward was set at 50 BTCs per block. However, every 210,000 blocks (roughly four years), this reward is reduced by half. This halving process continues until the block reward reaches its final destination of 1 satoshi (0.00000001 BTC), the smallest unit of Bitcoin.
The mathematical formula behind halving can be expressed as follows:
Halving Frequency = 210,000 blocks
Block Reward = Initial Reward / 2^(Number of Halvings)
With each halving, the number of new coins entering circulation is reduced, making it progressively harder and more resource-intensive for miners to earn rewards. This scarcity-driven model resembles the mining of precious metals like gold, where the supply is limited, and extracting new reserves becomes increasingly challenging over time.
The predictable and controlled reduction in block rewards ensures that the issuance of new coins remains gradual and steady. By adhering to this mathematical protocol, Bitcoin’s creator, Satoshi Nakamoto, sought to create a deflationary currency that would increase in value over time as its supply dwindles.
The significance of the mathematical principles governing halving lies in the controlled and predictable nature of Bitcoin’s monetary policy. This transparency and certainty have contributed to the cryptocurrency’s credibility and appeal as a store of value and a potential hedge against inflation.
Historical Analysis of Previous Bitcoin Halvings
Looking back at the previous halvings, we can observe the price and market trends before and after each event. Both halvings were followed by substantial price increases, sparking interest among investors and miners alike. We will analyze the factors that contributed to these price surges and assess the impact on miners and the broader Bitcoin ecosystem.
The historical analysis of previous Bitcoin halvings provides valuable insights into the cryptocurrency’s behavior and market trends surrounding these milestone events. Let’s delve into the two most recent halvings, which occurred in 2012 and 2016, to better understand their impact on the price of Bitcoin and the overall market.
The 2012 Halving: Early Signs of Bitcoin’s Potential
On November 28, 2012, the first Bitcoin halving took place, reducing the block reward from 50 coins to 25 coins per block. At the time of the halving, the price of a single Bitcoin was relatively modest, around $12.35. However, within 100 days, the price experienced a remarkable surge, reaching $42 per coin. The following year, it soared even further to an impressive $964.
This surge in price following the 2012 halving can be attributed to various factors. Firstly, the halving event itself garnered significant attention from the cryptocurrency community and the media, leading to increased interest and speculation. Additionally, the market sentiment at the time was bullish, with growing confidence in Bitcoin’s potential as a groundbreaking digital currency.
The 2016 Halving: Bitcoin’s Maturation and Price Surge
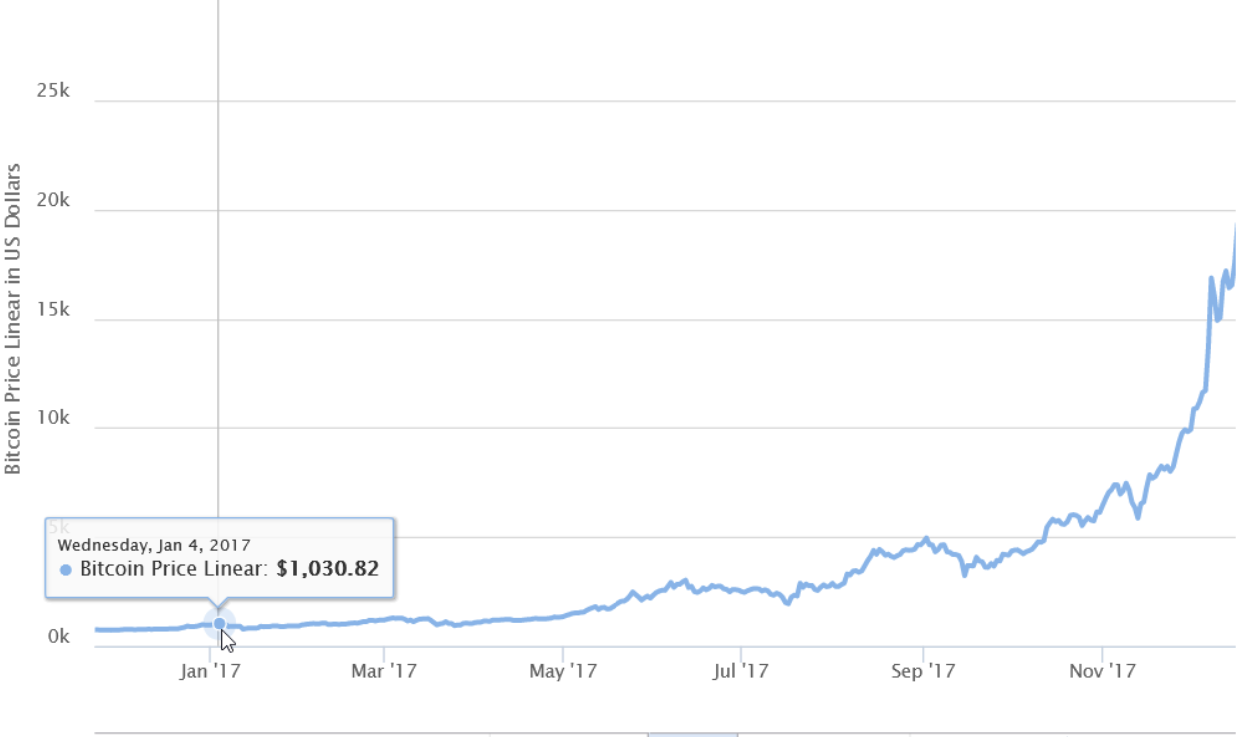
The second halving occurred on July 9, 2016, reducing the block reward from 25 coins to 12.5 coins per block. By this point, Bitcoin had gained more traction and visibility in the mainstream financial world. At the time of the halving, the price of a Bitcoin was around $650.63.
Following the 2016 halving, the price of Bitcoin experienced a similar upward trajectory. Within 100 days, the price had grown to nearly quadruple its value, reaching $2,550. The subsequent year saw even greater growth, with the price peaking at over $19,000 in December 2017.
The factors influencing the price surge after the 2016 halving were largely similar to those observed in 2012. The event generated significant hype and media coverage, capturing the attention of both seasoned investors and newcomers to the cryptocurrency space. Additionally, Bitcoin’s increasing adoption as a store of value and a speculative asset contributed to the surge in demand.
Check out our guide for further details on Bitcoin price and future predictions.
Impact On Miners And The Bitcoin Ecosystem
Bitcoin halvings not only affect the price but also have a profound impact on the mining community and the overall Bitcoin ecosystem. Mining is a critical process in the Bitcoin network, as miners validate transactions and add them to the blockchain while being rewarded with newly minted coins.
When the block rewards are halved, miners’ revenue is reduced, making mining less profitable for some participants. However, many miners are savvy and anticipate the halving events well in advance, adjusting their mining strategies to account for the reduced rewards. As a result, the network’s security remains robust, and mining activity continues.
Furthermore, the halving events have historically sparked renewed interest in mining, leading to an increase in the number of miners contributing their computational power to the network. This surge in mining activity further enhances the network’s security and resilience.
Factors Affecting Bitcoin Halving Dates
The occurrence of Bitcoin halving events is not tied to specific calendar dates but rather determined by specific factors within the cryptocurrency’s protocol. By understanding the key elements influencing the timing of halving events, we can better predict the approximate date of the next halving and its impact on the Bitcoin ecosystem. In this session, some of the key factors driving the Bitcoin halving dates will be analyzed.
Block Time
Block time refers to the time taken to mine a new block on the Bitcoin blockchain. The protocol is designed to maintain a consistent block time of approximately 10 minutes. However, in reality, block times can vary due to fluctuations in network activity and hashing power.
If the average block time is slightly less than 10 minutes, more blocks are mined within a given period, leading to a shorter time between halving events. Conversely, if block times exceed 10 minutes, the time between halvings lengthens. This variability is intrinsic to the decentralized nature of Bitcoin.
Hashing Power
Hashing power, also known as the network’s total computational power, plays a significant role in determining the speed at which new blocks are added to the blockchain. When hashing power increases, more blocks are mined in a shorter period, potentially leading to an early halving event.
Conversely, a decrease in hashing power may result in longer block times and a delay in the halving process. Changes in hashing power can be influenced by various factors, including the number of miners participating in the network, advancements in mining hardware, and the overall profitability of mining.
Network Difficulty Adjustments
To maintain the 10-minute block time target, the Bitcoin protocol adjusts the mining difficulty every 2016 blocks (approximately every two weeks). This difficulty adjustment mechanism is crucial in ensuring the stability and security of the network.
When hashing power increases, making block mining faster, the difficulty adjusts upwards to slow down block production. Conversely, if hashing power decreases, the difficulty adjusts downwards to facilitate faster block mining.
The interplay between hashing power and difficulty adjustments can impact the timing of halving events. If hashing power increases significantly during a certain period, blocks may be mined faster, potentially bringing the halving date forward. Conversely, a decrease in hashing power could push the halving date further into the future.
Estimating The Next Bitcoin Halving Date
The next Bitcoin halving is a highly anticipated event within the cryptocurrency community, as it has historically impacted the market and generated substantial interest among investors and enthusiasts. To estimate the likely date of the upcoming halving, analysts and experts rely on live blockchain data and employ various predictive models and methodologies.
One approach to estimating the next halving date involves monitoring the average block time over a specific period, typically the past two months. By analyzing this data, analysts can calculate the average time it takes to mine a new block. As the Bitcoin protocol is designed to produce a block approximately every 10 minutes, this average block time provides crucial insights into the network’s current mining speed and efficiency.
Once the average block time is determined, analysts can project the number of blocks remaining until the next halving. As halving events occur after every 210,000 blocks, dividing the remaining blocks by the average daily blocks mined provides an approximate time frame for the upcoming halving.
However, it is essential to acknowledge that accurately predicting the halving date comes with certain challenges and uncertainties. Bitcoin’s decentralized nature and the dynamic nature of hashing power and mining difficulty can lead to fluctuations in block time. Additionally, unforeseen changes in network activity or hashing power can impact the estimation process.
Despite these challenges, expert analyses and sophisticated predictive models provide valuable insights into when the next halving is likely to occur. As the Bitcoin network continues to grow and evolve, the countdown to the next halving remains an exciting aspect of the cryptocurrency market, with many eagerly awaiting its arrival to witness its potential impact on the price, mining ecosystem, and the broader adoption of Bitcoin as a digital asset with limited supply.
Expert Opinions On The Next Halving
As the upcoming Bitcoin halving approaches, experts and analysts are closely watching its potential impact on the market and the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Some believe it could lead to another surge in Bitcoin’s price, driven by reduced block rewards and steady demand. Others argue that the market has matured, possibly dampening the price impact.
Institutional investors’ role and external factors like regulations and economic conditions will also be assessed. The opinions vary, making it essential to consider diverse viewpoints and expert analysis when evaluating the halving’s potential consequences in the dynamic and complex cryptocurrency landscape. Nevertheless, there’s no doubt about Bitcoin being one of the best cryptocurrencies to buy now.
Potential Effects Of The Next Halving
The next Bitcoin halving is anticipated to be a milestone event with potential far-reaching effects on the cryptocurrency market.
As we delve into its implications, we will consider various aspects that could be influenced by this significant event.
Bitcoin’s Price: Historically, Bitcoin’s price has experienced considerable upward pressure after previous halvings. The reduction in the block reward decreases the rate at which new coins are created, leading to a decreased supply. Given steady demand, this supply scarcity could result in a price surge, driving Bitcoin’s value higher.
Volatility: The halving event may also contribute to increased market volatility. As traders and investors react to the uncertainty surrounding the event’s impact, price swings and heightened trading activity can be expected in the days and weeks leading up to and following the halving.
Mining Profitability: With the block reward halved, miners’ revenue from newly minted coins will decrease. Mining profitability may be affected, especially for those operating with older or less efficient hardware. However, if the price of Bitcoin rises significantly, it could offset the reduced block reward and maintain miners’ incentives to participate in securing the network.
Network Security: Bitcoin’s security relies on miners’ participation in validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain. While halvings may reduce miners’ revenue, it is essential to consider the long-term implications for network security. If the value of Bitcoin increases over time, miners’ rewards in terms of fiat currency may still be substantial, ensuring their continued participation in securing the network.
How To Prepare For The Next Halving
Preparing for the next Bitcoin halving requires careful planning and awareness of the potential market impacts. For investors and traders, staying informed about the latest market trends and expert analyses is crucial. Diversifying investments and setting realistic goals can help mitigate risks associated with increased volatility.
Miners and mining pools should closely monitor network difficulty and adjust their operations accordingly. Optimizing mining strategies and considering long-term profitability will be essential in the face of reduced block rewards.
Staying informed and making well-informed decisions will be paramount as the halving event approaches. Understanding the potential effects and being prepared to adapt to changing market conditions will be key for all stakeholders in the crypto space.
Preparing For The Future Of Bitcoin Halving
The next Bitcoin halving is a highly anticipated event that has historically impacted the cryptocurrency market. Understanding the mathematics behind halving, analyzing historical trends, and estimating the date of the next halving are essential steps in preparing for its potential effects. Experts’ opinions will further shed light on the event’s significance, guiding investors and enthusiasts alike in navigating the ever-evolving world of Bitcoin.
As the cryptocurrency space continues to evolve, staying updated with expert analysis and keeping track of halving events will be crucial in making informed decisions and capitalizing on the opportunities presented by the next Bitcoin halving.
Whether you are a seasoned investor or a curious newcomer, the next halving is an event to watch closely, as it can shape the future of the cryptocurrency market. Looking to buy buy Bitcoin ahead of the highly-anticipated event? Read our guide on how to buy cryptocurrency safely.
Conclusion
There’s no doubt that Bitcoin is the most successful crypto in the market, thanks to its scarcity-driven model. The adoption of this monetary model by Bitcoin founder, Satoshi Nakamoto has continued to drive its appeal and value, positioning it as a viable medium of payment. Check our guide to discover some of the best companies that have adopted Bitcoin for payments.
Meanwhile, in this guide, we covered and dissected everything you need to know about the next Bitcoin halving. Driven by the price trends that greeted the previous halving events, there is a real buzz around the next one that has been billed to unfold in 2024. Investors remain optimistic the much-anticipated event will trigger the next crypto bull run.
Are you on the lookout for the best place to buy Bitcoin and altcoins ahead of the next bull run? Check out eToro.
FAQs
What will happen when all the BTCs are mined?
When all the BTCs are mined, which is projected to occur around the year 2140, the total supply of Bitcoin will reach its maximum limit of 21 million coins. At this point, no new Bitcoin will be created through mining. Miners will rely solely on transaction fees for their rewards, and the scarcity of Bitcoin may potentially increase its value.
What are the impacts of halving on BTC?
Bitcoin halving events, which occur approximately every four years, have significant impacts on the cryptocurrency market. The reduction in block rewards leads to a decrease in the supply of newly minted Bitcoins, making them scarcer. This scarcity-driven model, coupled with steady demand, has historically resulted in price surges following halving events.
Can halving lead to mining centralization?
Halving events can potentially influence mining centralization. As block rewards decrease, smaller and less efficient miners might find it challenging, leading to consolidation among larger and more powerful mining operations. However, the impact on mining centralization also depends on other factors, such as advancements in mining technology and overall market conditions.
Can halving lead to increased transaction fees?
After each halving, the block rewards decrease, which may lead to higher transaction fees. As miners receive fewer newly minted coins, they may rely more on transaction fees as an incentive to prioritize certain transactions. This could result in increased fees, especially during periods of high network activity.